

Time to start thinking inside the box! The Corrigan Cube can be used to read Base-2 (binary), Base-4 (quaternary), and Base-16 (hexadecimal) without much effort at all.
This is because each shape has a mark that it is an “equivalent” of it, so to speak. This will be extremely important while multiplying.
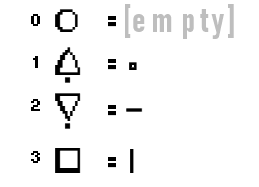
So to read the Corrigan Cube, choose a shape and a mark. The shape will come first, and the mark second.
An up-triangle with a vertical-mark…
In binary would be 01 & 11 = 0111
In quaternary would be 1 & 3 = 13
in hexadecimal would be 4 + 3 = 7



